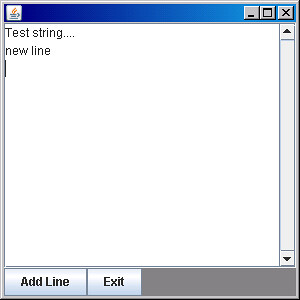
通常一個視窗中會有多個不同的按鈕,點下按鈕後,按鈕會分別有不同的動作。
假設我們寫了一個 JTextArea 讓使用者輸入資料,當按下「Add Line」按鈕時會自動換行,按下「Exit」按鈕時會結束程式。
程式碼:
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class panel0 {
JFrame frame = new JFrame();
JPanel panel = new JPanel();
JButton b1 = new JButton("Exit");
JButton b2 = new JButton("Add Line");
JTextArea text = new JTextArea(5,10);
JPanel panelControl = new JPanel();
public static void main(String[] arg){
panel0 gui = new panel0();
gui.go();
}
public void go(){
panel.setBackground(Color.gray);
panel.setLayout(new BoxLayout(panel,BoxLayout.Y_AXIS));
panelControl.setBackground(Color.gray);
panelControl.setLayout(new BoxLayout(panelControl,BoxLayout.X_AXIS) );
text.setLineWrap(true);
JScrollPane scroller = new JScrollPane(text);
scroller.setVerticalScrollBarPolicy(ScrollPaneConstants.VERTICAL_SCROLLBAR_ALWAYS);
scroller.setHorizontalScrollBarPolicy(ScrollPaneConstants.HORIZONTAL_SCROLLBAR_NEVER);
b1.addActionListener(this);
b2.addActionListener(this);
text.setText("Test string....n");
panel.add(scroller);
panelControl.add(b2);
panelControl.add(b1);
frame.getContentPane().add(BorderLayout.CENTER,panel);
frame.getContentPane().add(BorderLayout.SOUTH,panelControl);
frame.setSize(300,300);
frame.setVisible(true);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
if( e.getSource() == b1 )
System.exit(0);
else
text.append("new linen");
}
}因為 JButton 所呼叫的 ActionListener 都會呼叫 actionPerfomed(),所以只好在此函式內判斷到底是哪個按鈕呼叫的,在依照不同的來源執行不同的動作。
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
if( e.getSource() == b1 )
System.exit(0);
else
text.append("new linen");
}但是這樣寫一點會使的整個程式架構混亂,尤其是按鈕需要值型的動作很複雜時,以後要維護程式碼會變的很麻煩,因此要換一個方式來做。
Java 中有個東西叫做 inner class,也就是 class 中的 class。 Inner class 可以存取 outer class 中的變數和函式,但是要注意的是 inner class 是當 outer class 被建立時才會跟著一起被建立,不會單獨存在。
這時要為每個 JButton 建議一個 inner class:
class buttonListenerEXIT implements ActionListener{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
System.exit(0);
}
}
class buttonListenerNewLine implements ActionListener {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
text.append("new linen");
}
}建立好 inner class 之後,要讓 JButton 的 ActionListener 會去呼叫寫好的函式:
b1.addActionListener(new buttonListenerEXIT());
b2.addActionListener(new buttonListenerNewLine());改好之後,整個程式會變成這樣:
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class panel0 {
JFrame frame = new JFrame();
JPanel panel = new JPanel();
JButton b1 = new JButton("Exit");
JButton b2 = new JButton("Add Line");
JTextArea text = new JTextArea(5,10);
JPanel panelControl = new JPanel();
public static void main(String[] arg){
panel0 gui = new panel0();
gui.go();
}
public void go(){
panel.setBackground(Color.gray);
panel.setLayout(new BoxLayout(panel,BoxLayout.Y_AXIS));
panelControl.setBackground(Color.gray);
panelControl.setLayout(new BoxLayout(panelControl,BoxLayout.X_AXIS) );
text.setLineWrap(true);
JScrollPane scroller = new JScrollPane(text);
scroller.setVerticalScrollBarPolicy(ScrollPaneConstants.VERTICAL_SCROLLBAR_ALWAYS);
scroller.setHorizontalScrollBarPolicy(ScrollPaneConstants.HORIZONTAL_SCROLLBAR_NEVER);
b1.addActionListener(new buttonListenerEXIT());
b2.addActionListener(new buttonListenerNewLine());
text.setText("Test string....n");
panel.add(scroller);
panelControl.add(b2);
panelControl.add(b1);
frame.getContentPane().add(BorderLayout.CENTER,panel);
frame.getContentPane().add(BorderLayout.SOUTH,panelControl);
frame.setSize(300,300);
frame.setVisible(true);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
class buttonListenerEXIT implements ActionListener{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
System.exit(0);
}
}
class buttonListenerNewLine implements ActionListener {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
text.append("new linen");
}
}
}